Chapter 12 Software development
12.1 Program development lifecycle
Program development lifecycle – the process of developing a program set out in five stages:
- analysis
- design
- coding
- testing
- maintenance
Waterfall model – a linear sequential program development cycle, in which each stage is completed before the next is begun
- pros: easy to manage
- cons: not suitable for long, complex projects; difficult to change the requirements at a later stage
Iterative model – a type of program development cycle in which a simple subset of the requirements is developed, then expanded or enhanced, with the development cycle being repeated until the full system has been developed
- pros: easier to test and debug smaller programs; more flexible as easier to alter requirements
- cons: not suitable for short simple projects
Rapid application development (RAD) – a type of program development cycle in which different parts of the requirements are developed in parallel, using prototyping to provide early user involvement in testing
- pros: reduced overall development time; very flexible as requirements evolve from feedback during development
- cons: system under development needs to be modular; not suitable for short simple projects
12.2 Program design
Structure chart – a modelling tool used to decompose a problem into a set of sub-tasks. It shows the hierarchy or structure of the different modules and how they connect and interact with each other
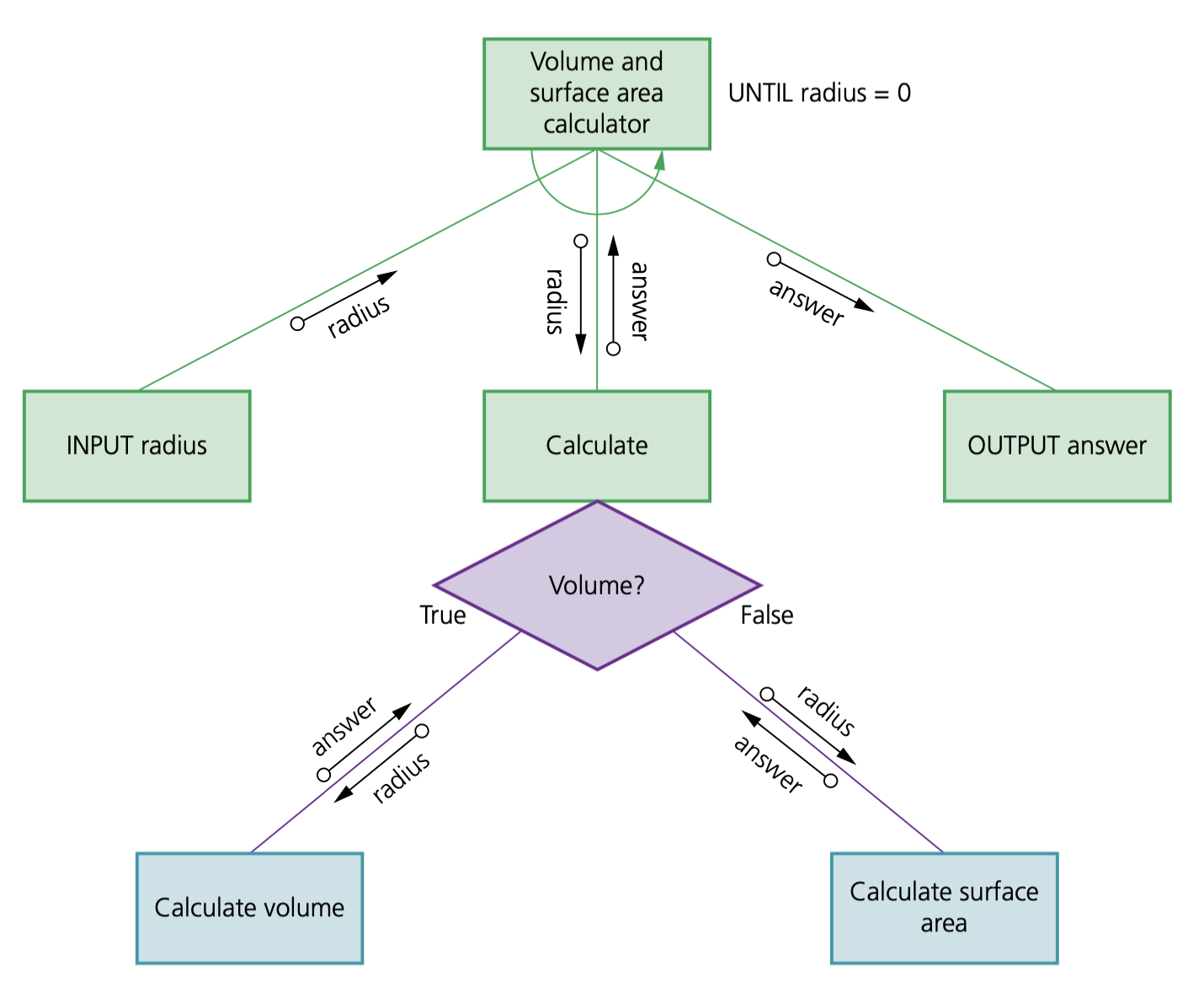
DECLARE radius : REALDECLARE answer : REALCONSTANT pi ← 3.142FUNCTION calculateVolume (radius:real) RETURNS realRETURN (4 / 3) * pi * radius * radius * radiusENDFUNCTIONFUNCTION calculateSurfaceArea (radius:real) RETURNS realRETURN 4 * pi * radius * radiusENDFUNCTIONPROCEDURE inputRadiusOUTPUT "Please enter the radius of the sphere "INPUT radiusWHILE radius < 0 DOOUTPUT "Please enter a positive number "INPUT radiusENDWHILEENDPROCEDUREPROCEDURE outputAnswerOUTPUT answerENDPROCEDURECALL inputRadiusWHILE radius <> 0OUTPUT "Do you want to calculate the Volume (V) or Surface Area (S)"INPUT replyIF reply = "V"THENanswer ← calculateVolume(radius)OUTPUT "Volume "ELSEanswer ← calculateSurfaceArea(radius)OUTPUT "Surface Area "ENDIFCALL outputAnswerCALL inputRadiusENDWHILE
A finite state machine (FSM) is a mathematical model of a machine that can be in one of a fixed set of possible states. One state is changed to another by an external input, this is called a transition. A diagram showing the behaviour of an FSM is called a state-transition diagram.
12.3 Program testing and maintainence
Trace table – a table showing the process of dry- running a program with columns showing the values of each variable as it changes Run-time error – an error found in a program when it is executed; the program may halt unexpectedly
Program testing
Several types of test data need to be used during testing:
- Normal test data
- Abnormal test data that should be rejected by a program as it is unsuitable or could cause problems
- Extreme test data - data on the limit of that accepted by a program
- Boundary test data - data on the limit of being accepted by a program or just outside the limit of being accepted
Testings as the program is being developed:
- White-box testing - the detailed testing of how each procedure works. This involves testing the structure and logic of every path through a program module
- Black-box testing - tests a module’s inputs and outputs
- Integration testing - the testing of any separately written modules to ensure that they work together, during the testing phase of the program development lifecycle
When the program has been completed:
- Alpha testing - The completed, or nearly completed, program is tested in-house by the development team
- Beta testing - The completed program is tested by a small group of users before it is generally released
- Acceptance testing - used for the completed program to prove to the customer that it works as required in the environment in which it will be used
Program maintenance
- Corrective maintenance - used to correct any errors that appear during use
- Perfective maintenance - used to improve the performance of a program during its use
- Adaptive maintenance - used to alter a program so it can perform any new tasks required by the customer